If you’re looking to move your hosted services from on-premise to the cloud, you have three main options: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS.
With all three cloud computing models having distinct advantages and use cases, many companies face dilemmas when choosing between the three.
So, in this article, we will explore the key differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, alongside their pros, cons, and use cases, to help you make the right decision for your business.
What are SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS?
SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are three different types of cloud computing service models.
All three services provide computing resources for you to develop and host your web applications or services on the internet.
As such, the key advantages of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are cost-effectiveness and ease of use. You can easily access and use these services without having to host, maintain, and manage the hardware and other computing resources on-premise.
Here’s what SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are:
- Software as a Service (SaaS), also known as cloud application services, is a method for delivering cloud-based applications over the internet.
- Platform as a service (PaaS), sometimes called cloud platform services, is a cloud-based platform where you can develop, test, and manage apps.
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), or cloud infrastructure services, is a cloud-based service that provides users with the full set of resources needed to collaborate on projects, test, develop and deploy apps, and more, all through virtualization.
Although SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS deliver different services, it doesn’t mean that you have to choose only one of them. In fact, many businesses use two or all three models at the same time.
SaaS: Software as a Service
SaaS is perhaps the most commonly used type of cloud computing.
Put simply, SaaS companies provide software that users can access via a web browser. This eliminates the need for users to download and install your applications on their devices.
Most SaaS businesses use the recurring subscription revenue model and offer their apps for a monthly fee.
Advantages of SaaS
SaaS applications are popular not without good reason. Here are the main advantages of SaaS:
- Easy to use. To use a SaaS app, all you have to do is access it through a web browser.
- Accessibility. You can access SaaS apps from any device as long as it’s connected to the internet.
- Scalability. SaaS products are easily scalable – all you need is to simply upgrade your subscription plan.
Disadvantages of SaaS
Despite the advantages, SaaS comes with some limitations and downsides, which include:
- Limited integrations. Many SaaS solutions don’t offer open integrations, so users might find it difficult to find apps that seamlessly integrate with others.
- Limited customization. SaaS apps are ready-to-use and while this is convenient, it often means that users don’t have many options for customizing them to fit their specific needs.
- Minimal control. When customers use a SaaS app, they are giving all of the control to the SaaS vendor—including access to data. For this reason, it’s important to establish a secure connection between your customers and your software.
SaaS Delivery
As mentioned before, SaaS solutions are delivered over the internet. You can access them from virtually any web browser.
What’s more, SaaS service providers manage all aspects of the app: storage, data, middleware, runtime environments, networking, and more. Because of this, users can save money, as they don’t have to maintain the software themselves.
Use Cases for SaaS
SaaS apps are very versatile, so they can be used in a variety of situations. Some of the best use cases for the SaaS model include:
- Deploying your first application
- Selling software at a low monthly cost instead of a license fee
- Allowing access to applications both via web and mobile
SaaS Examples
Today, you can come across SaaS examples just about anywhere. Some of the most popular and most successful SaaS examples are:
- Dropbox – a file hosting app
- HubSpot – a CRM platform
- Zoom – a video conferencing platform
- Slack – a B2B messaging app
- Zendesk – a customer service app
Looking for more SaaS examples? Check out our SaaS database and gain insight into 32,000+ SaaS businesses.
PaaS: Platform as a Service
PaaS provides a platform where developers and DevOps teams can build, test, run, and manage customized apps over the internet. You can access the platform through a graphical user interface (GUI).
The following characteristics define PaaS as a cloud-based service:
- Scalability
- Accessibility to multiple users over the internet
- Built on virtualization technology
- Can be integrated with other web services
Advantages of PaaS
PaaS offers numerous advantages, including:
- Simplicity. Building, testing, running, updating, and scaling apps is much easier with PaaS than on your own on-premise platform.
- Speed. Because of its simplicity, PaaS enables teams to quickly develop and deploy apps.
- Collaboration. PaaS is a cloud-based service and thus allows development teams to work together from virtually anywhere, provided all users are connected to the internet.
Disadvantages of PaaS
PaaS also has several downsides that you should keep in mind, such as:
- Runtime issues. Sometimes PaaS solutions lack the support and optimization for specific frameworks and languages.
- Limited operations. PaaS solutions often have operational limitations for end-users and thus your PaaS solution might be incompatible with some operations.
- Legacy system integration issues. Integrating legacy IT systems that aren’t built specifically for the cloud with PaaS solutions can be challenging and time-consuming for users.
PaaS Delivery
Similarly to SaaS, PaaS delivers a service—a platform for software development—over the internet.
You can simply access the platform and build software via web browsers, without worrying about managing the hardware or operating systems. Users can then focus on managing their apps and data – while the rest is handled by the PaaS vendor.
Use Cases for PaaS
The primary use case for PaaS is software development. PaaS enables software developers to focus all of their time and energy on app development, as they don’t have to deal with software updates, patches, and such.
As a cloud-based service, PaaS facilitates collaboration. As such, it’s especially useful for teams of developers working on a single project.
PaaS Examples
Some of the most popular PaaS examples are:
- Heroku
- Microsoft Azure
- OpenShift
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Beanstalk
- Acquia Cloud
- Apprenda
- Cloudways
IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service
IaaS vendors provide users with an affordable, easy-to-use and maintain cloud-based alternative to on-premise IT infrastructure. With IaaS, customers don’t have to buy and manage hardware. If needed, they can easily purchase additional resources on-demand from the vendor.
IaaS is a very flexible and highly scalable solution that multiple users can access over the internet.
Advantages of IaaS
The main advantages of using IaaS include:
- Flexibility. IaaS is the most flexible type of cloud computing that allows users to build and scale services depending on their needs.
- Cost-effectiveness. Although IaaS solutions are often more expensive than PaaS and SaaS, they are still less expensive than buying and maintaining an on-premise IT infrastructure.
- Availability. IaaS enables customers to easily add on redundant servers to ensure their services are available at all times.
- Control. IaaS differs from SaaS and PaaS in terms of control, as users retain total control over the infrastructure instead of leaving it up to the cloud services vendor.
Disadvantages of IaaS
Here are the key disadvantages of IaaS you should be aware of:
- Training. IaaS provides more control than SaaS and PaaS, but with that also comes more responsibility. As such, businesses using IaaS have to allocate more resources for internal training to ensure that the IaaS services are correctly managed.
- Legacy system security. Users might have to upgrade or completely replace some legacy systems that aren’t compatible with the IaaS. This could potentially lead to security issues.
- Security. IaaS can be vulnerable to security threats, especially coming from the host and virtual machines (VMs). IaaS vendors need to secure the data of each individual customer, as IaaS typically uses the multi-tenant cloud architecture.
IaaS Delivery
The IaaS delivery model differs from SaaS and PaaS, as IaaS uses virtualization technology to deliver cloud-based infrastructure. IaaS clients access it through an API or a dashboard.
Because of this, IaaS gives you a ton of control over the infrastructure. This however means that you are responsible for managing apps, data, middleware, runtime, and the operating system of the IaaS.
However, unlike with traditional data centers, you don’t have to manage and maintain the cloud servers, storage, networking, and virtualization.
Use Cases for IaaS
IaaS is very flexible and scalable. Because of this, IaaS has many use cases and benefits all sorts of businesses.
Most common use cases for IaaS include:
- Ecommerce. IaaS is easily scalable, allowing online stores to accommodate large surges of traffic without experiencing any downtime.
- Small businesses and startups. IaaS is more affordable than on-premise data centers, which is why many new companies choose to use IaaS.
- Growth-stage companies. Because of its scalability, IaaS is the ideal option for businesses that are growing rapidly.
IaaS Examples
Most popular IaaS examples include:
- DigitalOcean
- Microsoft Azure
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Bluelock (acquired by InterVision)
- Google Cloud
SaaS vs Paas vs IaaS: What Are the Key Differences?
Now that you know what SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are, let’s find out the key differences between these three types of cloud computing.
Although they all deliver services over the internet, the services which they deliver are all different. SaaS is used for delivering apps, PaaS provides a platform for software development, and IaaS provides an entire computing infrastructure for users.
Moreover, the IaaS delivery model differs from SaaS and PaaS, as it uses virtualization technology to provide access to users through an API or a dashboard. Meanwhile, you can simply access SaaS and PaaS via your web browser.
Another key difference between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS is the level of management users get with each service:
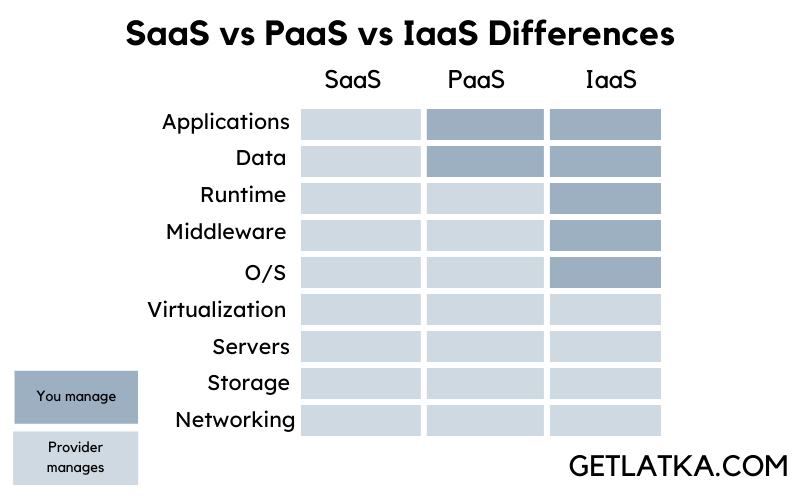
Simply put, SaaS service providers take control into their hands and fully manage the product for users. PaaS providers, on the other hand, manage everything except apps and data, which are in the user’s control.
IaaS vendors, meanwhile, let users manage most aspects of the IaaS service, such as the apps, data, runtime, middleware, and OS.
SaaS vs Paas vs IaaS: Which One Should You Choose?
As you might’ve noticed, SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS have different advantages and use cases. Which cloud computing model is the best for your business will largely depend on your goals.
SaaS is the best option for companies that are looking for an easy-to-use, out-of-the-box solution that doesn’t require any installations and maintenance on the user’s end.
If you’re looking for a platform specifically designed to build software, on the other hand, your best option is undoubtedly the PaaS model.
However, if you need a highly flexible and scalable solution that provides more control over the infrastructure, IaaS will be the ideal option.
You might also want to consider your budget. While all cloud-based services are much more affordable than on-premise, you should keep in mind that IaaS is the most expensive solution. SaaS, on the other hand, is the most affordable option out of the three.
That said, you can use SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS all at the same time for different purposes, too. As such, there’s no reason you should limit your options by choosing just one out of the three.
Conclusion
And that’s about all you need to know about IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Hopefully, now you have all the information you need to choose the best cloud computing model for your business.
SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are all types of cloud-based services that provide different advantages and use cases. The best option for your business will be the one that fits your needs and budget, but you can also use two or all three cloud computing models.
Most importantly, when choosing between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, you want to keep in mind the main difference between them: the level of control.
SaaS is fully managed by the service provider and thus provides users with minimal control, whereas IaaS gives users the most control over their service.